Different types of Ethernet cabling in Networking

Three companies DEC, Intel and Xerox together implemented Ethernet specification called the Ethernet Blue Book which was released in 1980. It was also known as the DIX standard after the company initials. Their first Ethernet LAN specification was used by IEE as 802.3committee. This was a 10 Mbps network that ran on coaxial cable, twisted pair and fiber optics cable. The IEE extended the 802.3 committees to three new committee knows as 802.3u (fast Ethernet), 802.3ab(Gigabit Ethernet on category 5), 802.3ae (10Gbps over fiber and coaxial cable).
This is a very important topic of CCNA which is very important Networking Training in current IT industry. Expertise in it will help in clearing Cisco certifications of CCNA route and switch exams.
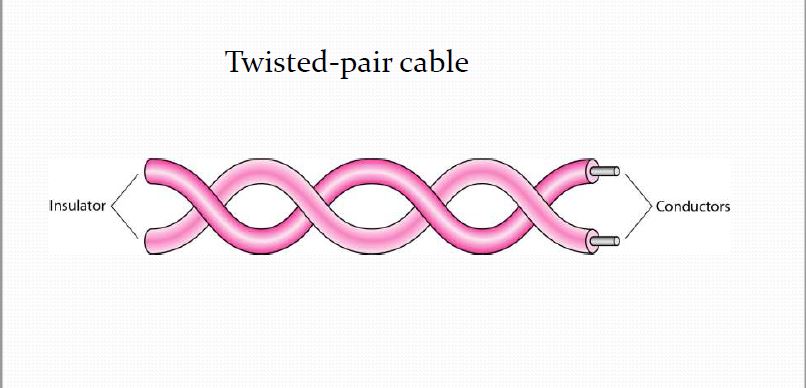
Twisted pair cable
Twisted pair cable contains of two conductors (normally both copper), each with its own plastic insulation, twisted around each other. The cable has pairs of wires with each pair twisted to eliminate electromagnetic interference and prevent crosstalk. Each pair forms a circuit which can transmit data. At each end of the cable RJ-45 connectors are installed.
There are two types of twister pair cables UTP and STP
(1) Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
Easy to install, expand, troubleshoot and is inexpensive. UTP cat 5 e replaced old coaxial cable which was unable to keep up with growing need of faster and more reliable networks. UTP is particularly susceptible to crosstalk, but the greater the number of twists per foot of cable, the more effective the protection against crosstalk.
CAT 1: UTP telephone cable that can carry voice but not data transmissions only telephone
Cat 2: Provides 4mpbs speed, used in Telephone lines
Cat 3: Provides 10mbps speed, used in LAN
Cat 4: Provides 16mbps speed, used in LAN and in token ring networks
Cat 5: Provides 100mbps speed. Ethernet, fast Ethernet used in LAN.
Cat 5e: Provides 1Gb speed, Gigabit Ethernet used in LAN
Cat 6: Provides 10Gbps speed, used in LAN
(2) Shielded twisted pair (STP)
STP cable has a metal foil covering that encases each pair of insulated conductors. The metal covering improves the quality of cable by preventing the penetration of noise or crosstalk. STP cable is more expensive and bulkier then UTP cable and is much more difficult to install and manage .
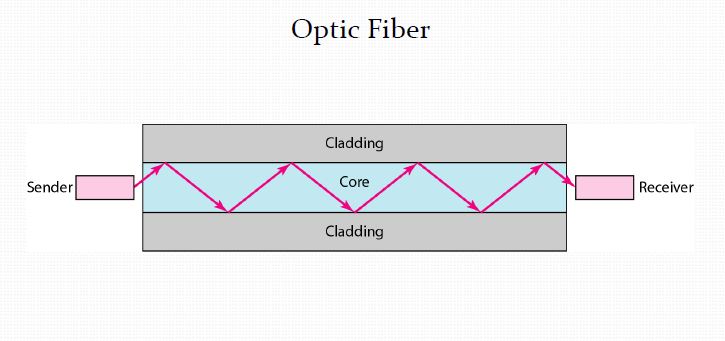
Fiber optic cable
These are used to provide high speed and fast transmission of data connectivity to long distances to link buildings, cities and countries. This cable is made of glass, is very thin and it carries digital data signals in the form of modulated pulses of light.Fiber optic cable is more expensive than other cables (coaxial or twisted pair cables). If the demand for bandwidth is not high, use of optical fiber cable cannot be justified. They are only used for high transmission rates.
Main components of the fiber optics cable are
- (a) Glass core: It holds the light. Example can be a size of 9 µ (9 micron)
- (b) Cladding: It confines the light in the core. Example can be a standard size of 125 µ (micron).
- (c) Buffer: It is there to protect the delicate glass. Example can be a size of 250 µ (micron).
Types of fiber optic cable
Single-mode
It is more expensive, has a tighter cladding and can go to farther distances than multimode. It can carry only one mode of light (very few light particles) across the fiber.
Multi-mode
It has a much looser cladding compared to single mode and a larger core hence it allows multiple light particles to travel down the glass.
Coaxial Cable
Co-axial cable has four layers. At the core is an inner conductor which is surrounded by a foam insulation, symmetrically surrounded by a woven braided metal shield, then covered in a plastic jacket. Because of its insulating property, coaxial cable can carry analogy signals with a wide range of frequencies. It’s hardly ever used in computer networks, but is widely used in cable television services and video connections, like those used by closed circuit surveillance systems.
Difference between cross cable and straight cable
Pc, router or server transmits from pin pair 1,2 and receives on pair 3.6.
Hub or switches transmits on pair 3,6 and receives on 1,2.

Codec Networks offers best CCNA Training in Delhi with best-experienced specialists. Codec Networks offers real-time and placement attentive computer Networking Training in Delhi Our hardware and networking development includes basic to advanced level and our computer networking course is planned to develop the assignment in good MNC companies in Delhi | NCR as quickly as once you whole the networking WAN, LAN training course.
You can read interesting CODEC Networks – Blogs to get more understanding :
.....................................................................................................................................................



Comments
Post a Comment